1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
191
192
193
194
195
196
197
198
199
200
201
202
203
204
205
206
207
208
209
210
211
212
213
214
215
216
217
218
219
220
221
222
223
224
225
226
227
228
229
230
231
232
233
234
235
236
237
238
239
240
241
242
243
244
245
246
247
248
249
250
251
| package org.example;
import static org.example.SinglelinkedList.*;
public class SingleLinkedListDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HeroNode heroNode1 = new HeroNode(1, "一号", "1号");
HeroNode heroNode2 = new HeroNode(2, "二号", "2号");
HeroNode heroNode3 = new HeroNode(3, "三号", "3号");
HeroNode heroNode4 = new HeroNode(4, "四号", "4号");
HeroNode heroNode5 = new HeroNode(4, "五号", "5号");
HeroNode heroNode6 = new HeroNode(6, "六号", "6号");
SinglelinkedList singlelinkedList = new SinglelinkedList();
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode1);
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode2);
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode3);
singlelinkedList.add(heroNode4);
singlelinkedList.list();
singlelinkedList.del(heroNode3);
singlelinkedList.list();
System.out.println("有效的节点个数:" + getLength(singlelinkedList.getHead()));
singlelinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode5);
singlelinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode6);
singlelinkedList.addByOrder(heroNode3);
singlelinkedList.list();
System.out.println("反转单链表-------");
reverseList(singlelinkedList.getHead());
singlelinkedList.list();
}
}
class SinglelinkedList {
public HeroNode getHead() {
return head;
}
private HeroNode head = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
public void add(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode temp = head;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
temp.next = heroNode;
}
public void addByOrder(HeroNode heroNode) {
HeroNode temp = head;
boolean flag = false;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.next.no > heroNode.no) {
break;
} else if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag) {
System.out.println("准备插入的编号已经存在,不能加入");
} else {
heroNode.next = temp.next;
temp.next = heroNode;
}
}
public void update(HeroNode heroNode) {
if (heroNode.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.no == heroNode.no) {
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag) {
temp.nickname = heroNode.nickname;
temp.name = heroNode.name;
} else {
System.out.println("未找到编号");
}
}
public void del(HeroNode heroNode) {
if (heroNode.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
boolean flag = false;
while (true) {
if (temp.next == null) {
break;
}
if (temp.next.no == heroNode.no) {
flag = true;
break;
}
temp = temp.next;
}
if (flag) {
temp.next = temp.next.next;
} else {
System.out.println("要删除的不存在");
}
}
public static int getLength(HeroNode head) {
if (head.next == null) {
return 0;
}
int length = 0;
HeroNode cur = head.next;
while (cur != null) {
length++;
cur = cur.next;
}
return length;
}
public static HeroNode findLastIndexNode(HeroNode head, int index) {
if (head.next == null) {
return null;
}
int length = getLength(head);
if (index <= 0 || index > length) {
return null;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
for (int i = 0; i < length - index; i++) {
temp = temp.next;
}
return temp;
}
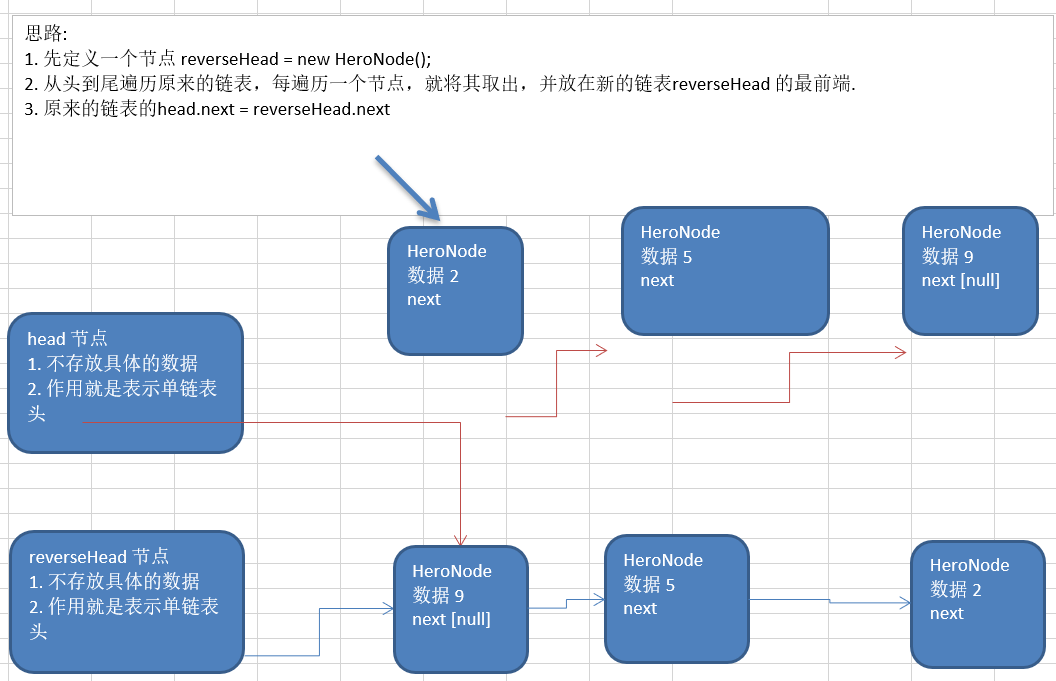
public static void reverseList(HeroNode head) {
if (head.next == null || head.next.next == null) {
return;
}
HeroNode cur = head.next;
HeroNode next = null;
HeroNode reverseHead = new HeroNode(0, "", "");
while (cur != null) {
next = cur.next;
cur.next = reverseHead.next;
reverseHead.next = cur;
cur = next;
}
head.next = reverseHead.next;
}
public void list() {
if (head.next == null) {
System.out.println("链表为空");
return;
}
HeroNode temp = head.next;
while (true) {
if (temp == null) {
return;
}
System.out.println(temp);
temp = temp.next;
}
}
}
class HeroNode {
public int no;
public String name;
public String nickname;
public HeroNode next;
public HeroNode(int no, String name, String nickname) {
this.name = name;
this.no = no;
this.nickname = nickname;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "HeroNode{" +
"no=" + no +
", name='" + name + '\'' +
", nickname='" + nickname + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
|